How can we help with the E-waste Problem?

Throughout the last decade, our society has become increasingly reliant on material belongings such as electronic devices, to keep up with the technological revolution. The E-waste generated when items are abandoned is a concern with this “continuous drive for more.” It’s the fastest increasing category of garbage in many countries since low costs mean replacing gadgets is cheaper than maintaining them, but low prices frequently mean inferior quality and short life spans. Top app development company in USA is finding ways to raise awareness regarding the matter.
What is E-waste?
According to a rubbish removal Sydney CBD expert, e-waste is broad term used for any electronic appliance that is thrown away, either in landfill, to be recycled or discarded. More specifically, it’s any waste that requires an electric current or electromagnetic field to work. Common examples of e-waste include devices such as mobile phones, radios, computers, white goods and batteries.
Statistical Data
A study reveals that 20-50 metric tons of e-waste is disposed off by people at a global level each year. A considerable portion of what is referred to as “e-waste” is good enough to be used for trading or can be reused for materials recovery. About 35,274 lbs. of copper, 772 pounds of silver, 75 lbs. of gold, and 33 lbs. of palladium may be recovered for each million cell phones reprocessed.
People buy more electronic gadgets because they desire more and because electronics have become a greater part of our life. As the number of electronic gadgets grows, so does the amount of electronic garbage create. As a society, we must recognize the risks that electronic gadgets represent to our health and the environment, as well as create and implement solutions to prevent these devices from filling landfills.
According to research by the UN global e-waste generation is on track to surpass 120 million tons per year by 2050 if present trends continue. Although the hazards of electronic trash are not obvious to the human eye, electronic waste poses health and environmental risks. Lead, mercury, arsenic, copper, silver, barium, chromium, nickel, zinc, and gold are all dangerous components in e-waste. Many of these components are found on circuit boards and include electrical components including computer chips, displays, and cables.
The challenges associated with E-waste
The most common form of improper electronic waste management is the open-air burning of electronics. Stacks of electrical gadgets are burnt in third-world nations to extract the valuable materials within, such as silver and gold.
Bio-magnification: When electronic waste is incorrectly disposed of, harmful compounds begin to accumulate in the environment and represent a hazard to our health through processes such as bio-magnification. Electronic waste’s chemical compounds bio-accumulate after being taken indirectly as food by species living in dumping places where electronic garbage is not adequately recycled. The buildup is since heavy metals included in electronic gadgets are difficult to break down; therefore, they remain in the system of the consumer for very long.
Affluent Spending: New technological breakthroughs influenced the way things were created and how people lived their lives in the early twentieth century. People’s aspirations for more, on the other hand, propelled these developments onward. Consumers in the pre-Depression era didn’t require as much as technological advancements permitted. The American people were frugal with their money. Over time, American businesses have changed their attention away from providing critical services and toward establishing new ones in order to boost consumer spending. Every year, tech heavyweights like Apple release a new product, yet there is no newness to be found.
E-Pollution
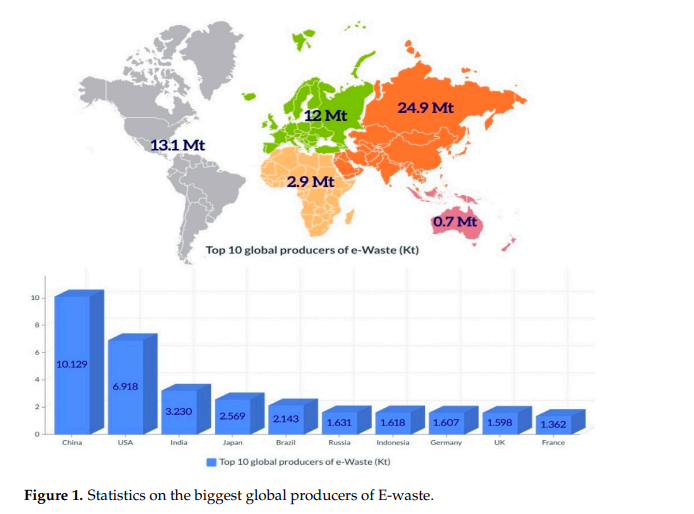
According to the United Nations, e-waste is the world’s fastest-growing rubbish source. China produced 11.1 million tons last year, while the US produced 10 million tons. While it is legal to export surplus equipment to needy countries if they can be recycled, lots of e-waste is being illegally shipped to Asia and Africa. According to a study, just 66 % of the millions of abandoned computers, monitors, televisions, and smartphones in the United States were recycled in the previous decade.
Health Menace: Improper e-waste disposal is extremely hazardous to the global ecosystem that is why it is critical to raise awareness about this rising problem and its potentially disastrous consequences. The consequences of these pollutants on humans include harm to the brain, kidneys liver, and other damage to the DNA.
Soil Pollutants
Electric particles produced after burning, shredding, or disassembling e-waste quickly re-deposit on the ground and pollute the soil. Climate, soil type, pH levels, and soil composition all have an impact on how much soil is polluted. These contaminants can persist continuously for a long time, posing a threat to soil microbes and plants.
Water-borne diseases: The e-waste and heavy metals push their way into wetlands reaching groundwater despite being just a few kilometres away from collection centres and dumping arenas. These toxins disrupt the ecosystem and pollute aquatic life. Acidification is yet another process that ruins the environment and affects underwater life while creating risks for seafood consumers. People unknowingly consume harmful matter and become victims of e-waste and the cycle continues.
Climatic impact: The impact of electronic products on global warming is alarming. Each gadget ever built has carbon emissions and contributes to global warming caused by humans. When considering the carbon dioxide emitted across a device’s lifespan, the majority of it happens during manufacture, before users purchase a product. This leaves a negative impact on the ecosystem and pollutes the air even before coming into use.
Resolving the Puzzle
Online storage system: It is a remedial technology that has the potential to “dematerialize” the electronics sector. International circular value chains might emerge as a result of the expansion of service marketing strategies and improved product monitoring. To address the demands of electronics supply chains, material efficiency, recycling infrastructure, and scaling up the volume and quality of recovered materials will all be necessary. If the correct policy combination is in place and the tech industry is handled properly. It has the potential to create excellent engagement throughout the world. A cloud computing architecture company in USA is undergoing research to create cloud computing a reliable venture.
Bridging the Gap by Activating Small Businesses
Linking informal and formal e-waste processors by giving awareness and opportunities to small and medium-sized firms. These are two significant solutions for more ecologically sound e-waste management in developing nations. Small and medium-sized businesses and industry groups can help enable collaboration. Throughout value chains, resulting in more circular and sustainable tech practices. The up-gradation of SMEs can better the situation by filling in the gap towards a circular economy.
The current scenario calls for immediate action to protect the millions of kids, adolescents, and expectant mothers. Whose health is jeopardised by the informal handling of abandoned electrical or electronic devices around the world.
Urban mining: The extraction of useful metallic components from the e-waste can result in halting the damage that the e-waste is causing today. Urban mining is basically the disposal of e-waste in a way. That any data present within the chips and devices is washed and products are recycled and refurbished.
A Circular Economy within the tech hub can be achieved by:
– Enabled sourcing of reusable tech material
– Increased longevity of tech products
– Revolutionise Consumer ideals by promoting durable goods
– Option of return back when a gadget no longer works
– Create a win-win for sellers and buyers by promoting nature-friendly goods
A circular economy with sustainable tech development can help tech enterprises make the world free of all hazardous waste. Environmental pollution and risks associated with e-waste are increasing day by day. An e-revolution that targets a safe ecosystem is the need of the hour.
For more information check www.xevensolutions.com!